Introduction
Ah grains, the base of the dreaded food pyramid. They get a lot of love, they get a lot of hate, but not much in the middle. Are grains good for you? Which ones? What nutrients do they provide? What if you're gluten free? I seek to answer all these questions today, and provide a grain of truth on the matter. As always, I am neither a doctor nor a nutritionist, just someone who's interested in nutrition science. Take everything I say with a grain of rice. I mean salt.
Other Posts in this Series

Contents


Amaranth is technically a pseudograin (like quinoa and buckwheat), but it is eaten much like a grain. It’s tiny, nutty, and gluten-free. A 1/4 cup (48 g) serving of raw amaranth provides 178 calories, 7 g of complete protein, 3 g of fiber, and 28 g of net carbs. Amaranth is one of the most nutritious grains, being rich in vitamin B1, vitamin B2, vitamin B5, folate, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, selenium, and zinc. Amaranth may help in regulating muscle and nerve function, combatting chronic inflammation, and supporting immune system health.
Serving Size: 1/4 cup (48 g)

Barley is one of the oldest cultivated grains, and a staple in soups, stews, and breads. Barley is a gluten containing grain, along with wheat and rye. It’s especially high in fiber, particularly beta-glucan, which can aid in lowering cholesterol and improving blood sugar control. 1/4 cup (50 g) of raw barley contains 176 calories, 5 g of protein, 8 g of fiber, and 39 g of net carbs. It’s also a good source of vitamin B1, vitamin B3, vitamin B6, copper, manganese, selenium, and zinc The glycemic index of barley is lower than most other grains due to it's high fiber content. It also is a good source of resistant starch, benefiting gut health.
Serving Size: 1/4 cup (50 g)

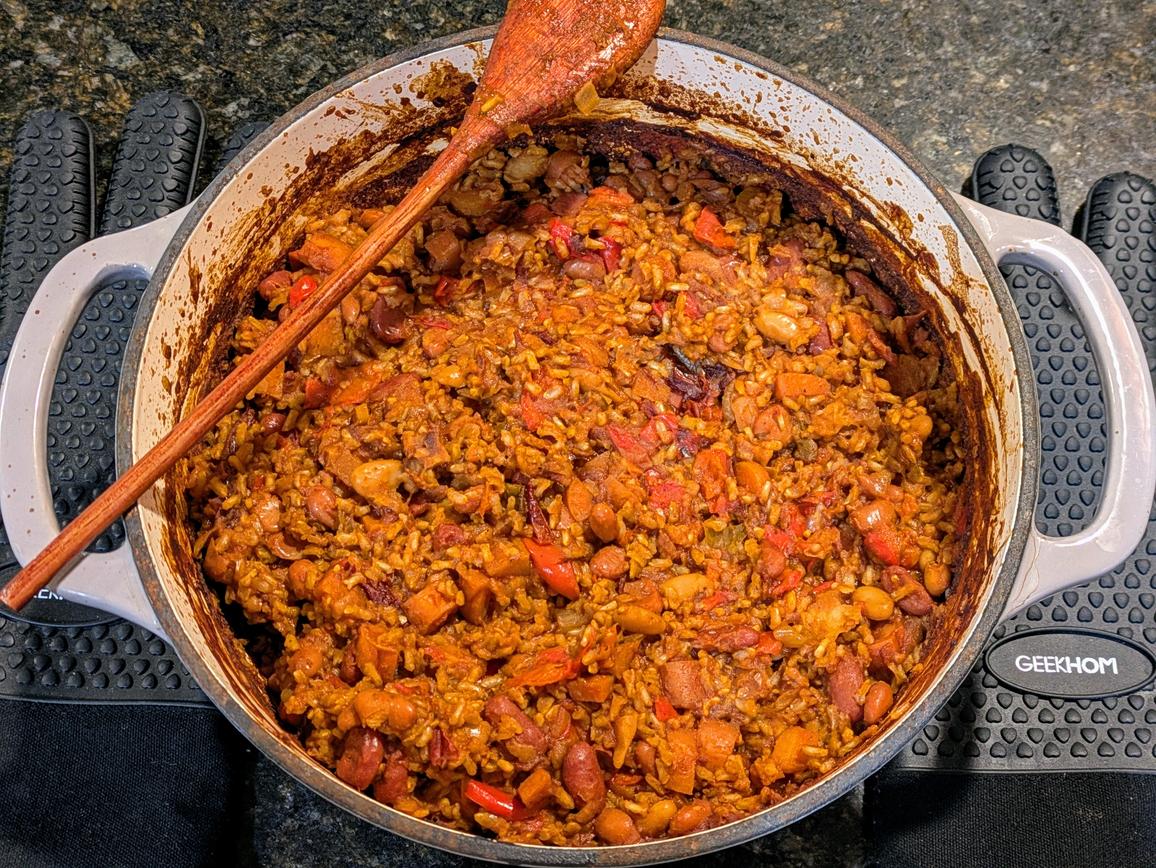
Brown rice is simply white rice with the bran and germ left intact, which makes it higher in fiber and nutrients. 1/4 cup (46 g) of raw brown rice has 169 calories, 4 g of protein, 2 g of fiber, and 35 g of net carbs. Brown rice is a gluten free grain that is quite nutritious, though less so compared to some other whole grains (like amaranth and barley). Brown rice provides vitamin B1, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, selenium, and zinc. It also has antioxidants and heart health benefits that are stripped away in white rice, while having a chewier texture and nuttier flavor.
There's no shortage of ways to include brown rice (or any other whole grains) in your diet. Typically, when I write recipes, I write them without a carb (so just a protein and vegetable), so that way you can add whatever starch you like on the side. Below are some recipes with brown rice, either as a side dish or mixed into the main:

Serving Size: 1/4 cup (46 g)

Buckwheat is another gluten free pseudograin, as are quinoa and amaranth. Despite the name, it’s not related to wheat at all; buckwheat is totally gluten free and also considered a complete protein. It's a moderate source of fiber, containing 4 g in a 1/4 cup (43 g) serving of raw buckwheat. Buckwheat is a strong source of vitamin B2, vitamin B3, vitamin B6, copper, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and zinc. It also contains unique compounds called rutin and quercetin, which act as powerful antioxidants that supports blood vessel health and reduce inflammation. Buckwheat also contains D-Chiro-Inositol, whch has a positive effect on managing blood sugar.
Serving Size: 1/4 cup (43 g)

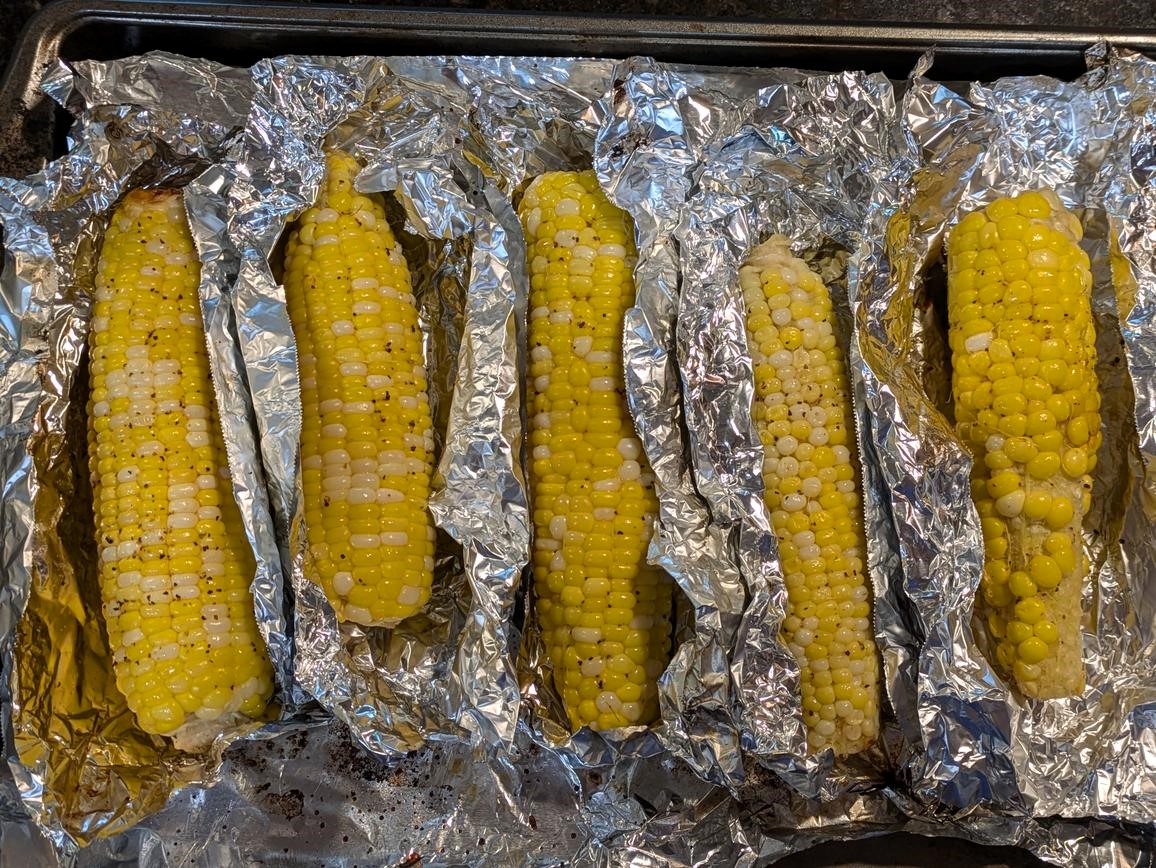
Corn is a staple gluten free grain that provides carbohydrates, some fiber, and antioxidants like lutein and zeaxanthin, which support eye health. Corn is quite lacking nutritionally, though it is one of the highest sources per gram of vitamin B6. That being said, whole corn and popcorn are much higher in nutrients than refined corn products, such as corn syrup, cornstarch, and corn oil. Just remember that corn is a grain/carb side, not a vegetable. I prefer to have my corn in the form of Roasted Corn on the Cob or Three Sisters - Squash, Beans, and Corn.

Serving Size: 3 oz (85 g)

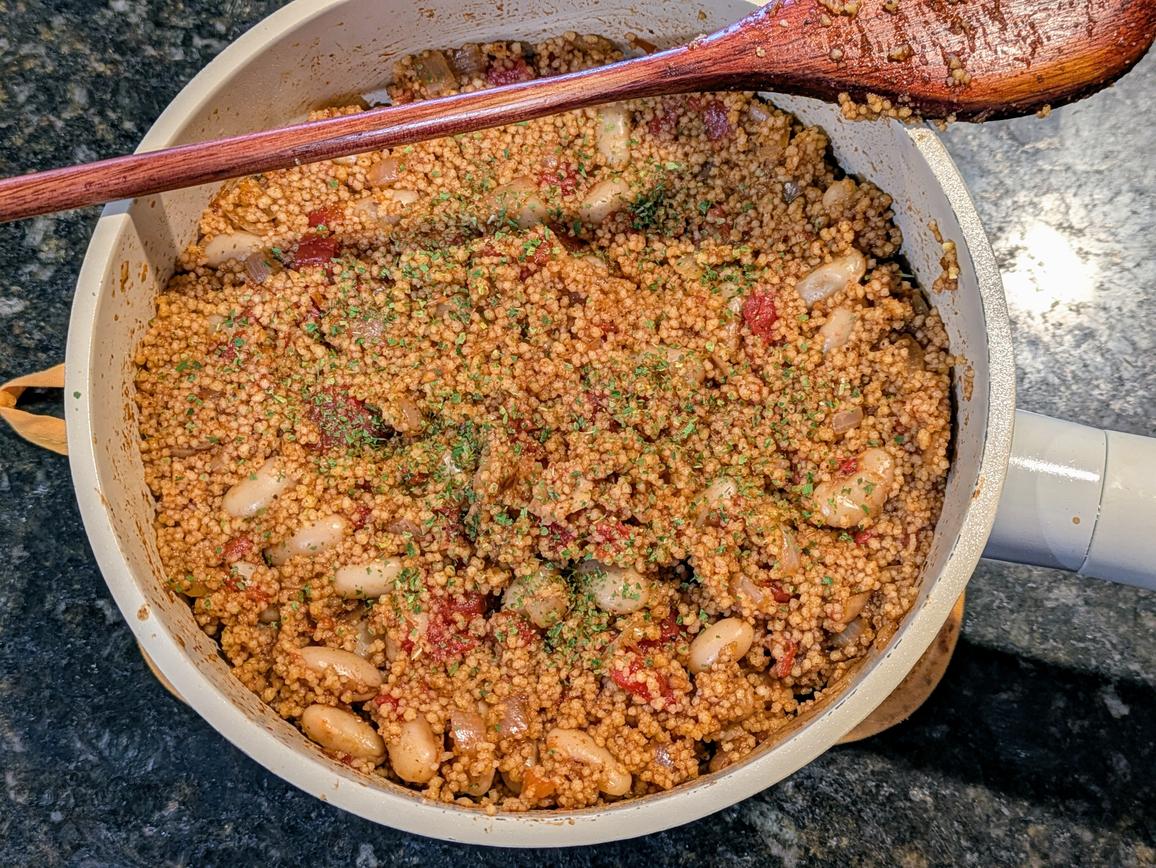
Couscous similar to many other grains, being a moderate source of the following nutrients: fiber, thiamin, niacin, vitamin B5, copper, magnesium, manganese, and phosphorus. These nutrients support energy metabolism, healthy digestion, and overall cell function, making couscous a light yet nourishing base for many meals.
Couscous is technically a pasta, being made of semolina wheat. That means that this delicious rice-like grain contains gluten. But it's more like rice than pasta; you cook couscous like you would rice, cooking until all the water has been absorbed. This is as opposed to pasta, which is boiled in excess water, and then subsequently drained off.
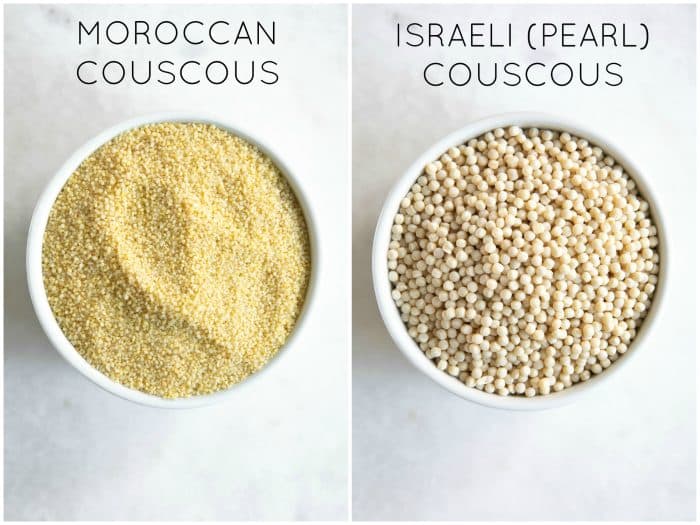

There's 2 different types of couscous: Moroccan and Israeli. Moroccan couscous is finer and fluffier, whereas Israeli (Pearl) couscous is bigger and more pasta-like. My preferred way to eat couscous is to cook Moroccan couscous with beans and diced tomatoes, like I do in my Tomato and Bean Couscous.

Serving Size: 1/4 cup (56 g)
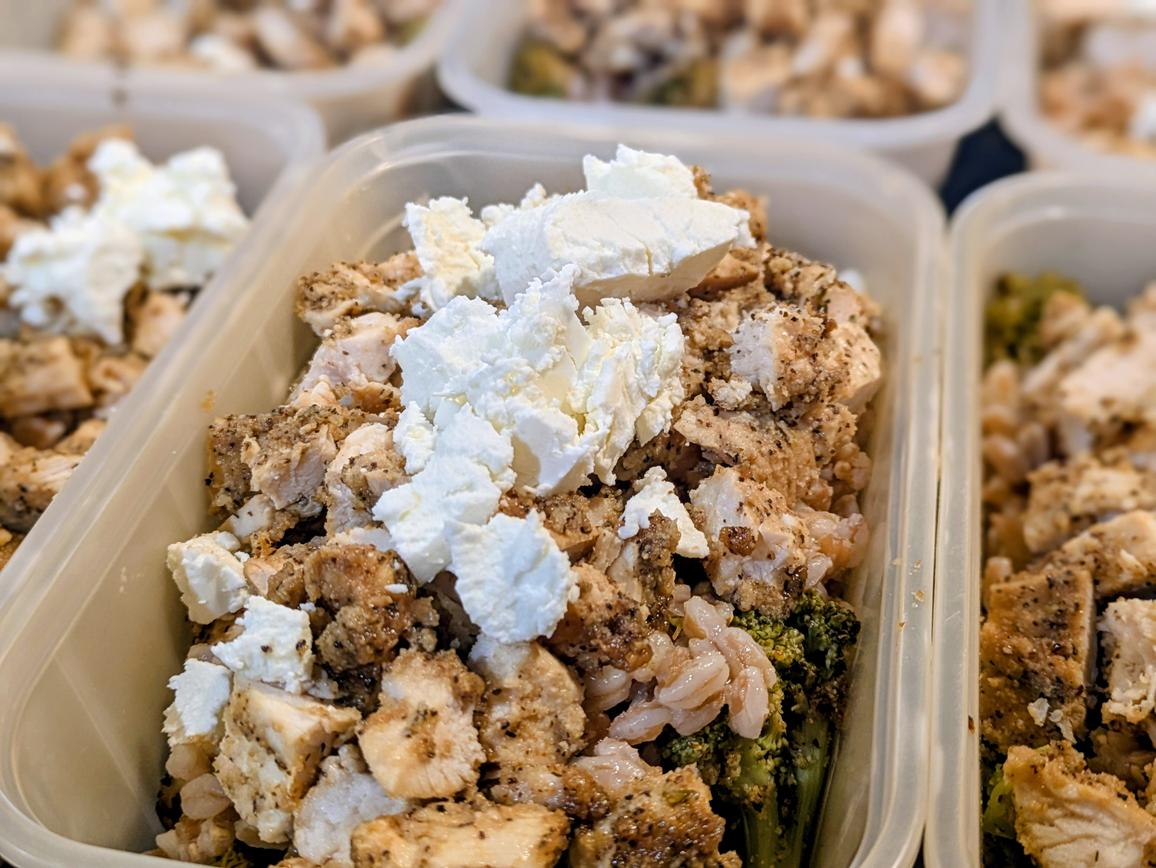
Farro is an ancient wheat based grain that cooks and tastes like brown rice. This gluten containing whole grain is a great addition to your diet, being high in fiber and protein for a side dish, as well as thiamin , niacin, vitamin B6, copper, magnesium, phosphorus, and zinc. Consider checking out my Chicken Farro Bowls with Goat Cheese for a delicious and complete meal featuring farro, with over 50 g of protein in under 550 calories.

Serving Size: 1/4 cup (45 g)
Millet is a gluten free grain high in vitamin B1, vitamin B2, vitamin B3, vitamin B6, folate, copper, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and zinc. It's a decent source of plant protein, with 6 g in a 189 calorie serving, as well as 4 g of fiber. It's lower glycemic index value may be helpful in combatting insulin resistance, and its carotenoids may benefit wound healing. As it's gluten free, millet flour is great in gluten free baking; see my Gluten Free Millet Bread for more.
Serving Size: 1/4 cup (50 g)

Ah, my beloved oats. Not only are they gluten free, but oats are rich in a fiber known as beta-glucan, which can help lower cholesterol and steady blood sugar levels. A 1/4 cup (40 g) of raw oats contains 4 g of fiber in just 152 calories, along with 5 g of protein. Oats are the best source of vitamin B1 and also contain notable amounts of vitamin B5, copper, iron, manganese, phosphorus, selenium, and zinc. Additionally, oats contain avenathramides, which are antioxidants linked to reduced inflammation and lower blood pressure.
I don't think there's an ingredient I use more in baking than oats, as long as you're not counting vanilla or salt or something. Between rolled oats, quick oats, and oat flour, oats are a staple part in my desserts, protein snacks, and breakfasts. Check out my myriad of recipes with oats below:
Serving Size: 1/2 cup (40 g)

When air-popped, popcorn is a great gluten free, whole grain snack that’s low in calories and high in fiber. Popcorn is one of the best volume foods, just 3 tbsp (40 g) of raw popcorn becomes over 7 cups of cooked popcorn. It also contains antioxidants like polyphenols, but it’s best without excess butter or salt. Check out my Healthy Microwave Popcorn for a significantly healthier alternative to movie theater or microwave popcorn, being free of tons of fat and added chemicals.
Serving Size: 3 tbsp (40 g)

Quinoa is a gluten-free pseudograin (like amaranth and buckwheat) notable for being a complete protein, as it contains all 9 essential amino acids. It’s surprisingly higher in protein (6 g) than fiber (3 g) with 158 calories in a 1/4 cup (43 g) serving. Quinoa is a good source of many B vitamins, such as B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, and B9. Quinoa is also rich in vitamin E, choline, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, selenium, and zinc. Quinoa is also a good source of the antioxidants kaempferol and quercetic, which help protect against chronic disease and lower inflammation.
Quinoa is one of the healthiest side dishes out there, and cooks just like rice in half the time. In any recipe calling for white or brown rice, you can simple swap them for quinoa for extra nutrition and a nuttier flavor. Check out my No Butter Chicken with Quinoa and Date Night Superfood Bowls for some quinoa based recipes.
Serving Size: 1/4 cup (43 g)

Rye, along with wheat and barley, is a gluten containing whole grain that provides a dense source of fiber (6 g) and protein (4 g) in 142 calories. The high fiber content in rye supports healthy digestion and aids in satiety, and rye can also help lower LDL levels. It is a good source of the vitamins B1, B2, B3, B6, and B9. Moreover, rye is a good source of copper, manganese, selenium, and zinc. It has a stronger flavor and may support better blood sugar control than refined wheat.
Serving Size: 1/4 cup (42 g)

Spelt is an ancient variety of wheat (meaning it's not gluten free) that contains fiber, protein, and minerals like copper, iron, manganese, selenium, and zinc. Like most other grains, spelt is a good source of B vitamins, notably B1, B3, B6, and B9. It still has gluten, but some find it easier to digest than modern wheat.
Serving Size: 1/4 cup (44 g)

Vital wheat gluten is the concentrated protein extracted from wheat. It's basically the anti gluten free flour; it's made up of entirely gluten. Vital wheat gluten is what gives seitan its chewy texture, and is very high in protein while being low in net carbs. Gram for gram, vital wheat gluten basically has the macros of protein powder, though the protein quality of gluten is extremely poor.
In bread making though, vital wheat gluten is a great ingredient that leads to a lighter, fluffier loaf. When swapping out white flour in place of whole wheat, I like to add a little vital wheat gluten to the dough, which results in a less dense loaf of bread. Below are a few recipes utilizing vital wheat gluten:

Serving Size: 1/4 cup (30 g)

White flour is to whole wheat flour what white rice is to brown rice. Besides white flour, it's also known under the names all purpose flour, bread flour, cake flour, etc. As with white rice, white flour needs to be enriched with vitamins and minerals, because they've all been stripped away. White flour has little to no fiber and has a glycemic index of 85, higher than white sugar! And as you are likely aware, white flour contains gluten.
Serving Size: 1/4 cup (31 g)

White pasta is a refined wheat-based grain product that contains gluten. A typical serving of pasta consists about about 3/4 cup (2 oz, 56 g) of raw pasta, or about 2 cups (135 g) of cooked pasta. Each serving contains about 200 calories with 2 g fiber and 7 g of protein. Being a refined white flour grain product, standard white pasta is nutritionally quite lacking, containing more empty calories than actual nutrition. Compared to whole wheat pasta, white pasta is significantly lower in B vitamins, iron, magnesium, and potassium.
Serving Size: 3/4 cup (56 g)
White rice is a gluten free refined grain with most of its fiber and micronutrients removed. White rice is often enriched with vitamins and minerals. Do you know why? Because it's so devoid of them in the first place. All the health benefits of the whole rice grain have been stripped away, leaving nothing but refined white starch with a low fiber content and a high glycemic index. When in doubt, swap out white for brown rice.
Serving Size: 1/4 cup (49 g)

Whole wheat flour retains the bran and germ, unlike white flour, making it higher in fiber and lower in net carbs. Containing all the nutrients of the whole wheat kernel, whole wheat flour is a rich source of vitamin B1, vitamin B3, vitamin B6, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, selenium, and zinc. Whole wheat supports digestive health and provides steadier blood sugar control compared to refined wheat. It also contains phenolic compounds known as lignans and tocopherols, which can help combat chronic inflammation. Whole wheat flour does contain gluten, so be on the lookout for that if you have Celiac.
I will always swap out white flour whole wheat for better nutrition and taste. In bread making, I like to add a little vital wheat gluten to the dough, which results in a less dense loaf of bread. Below are a few recipes utilizing whole wheat flour:

Serving Size: 1/4 cup (31 g)

Whole wheat pasta is a less refined wheat-based grain product that contains gluten. When considering pasta options, whole wheat pasta is a signifcantly better source than standard white pasta. Whole wheat pasta contains triple the amount of fiber, leading to less net carbs and calories.
Additionally, whole wheat pasta is a moderate source of B vitamins, such as B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, and B9. Whole wheat pasta is a good source of many minerals, namely copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, selenium, and zinc.
The typical way to eat pasta would be as a side dish with a sauce on top of it. Classic options include my Simple Pasta Sauce, Creamy Pesto Dip, Lightened EVOO Pesto, Avocado Pesto, Oil Free Bail Pesto, Pesto Classico, and Gooey Cheese Sauce.

As for other pasta based dishes, whole wheat pasta can be a great basis for many meals, namely a Penne and Meat Casserole Bake, Two Ingredient Mac & Cheese, or Viral Baked Feta Pasta.

When I'm choosing a pasta though, I'll typically opt for either red lentil or chickpea pasta. Not only are these both gluten free, but legume based pastas are more nutrient dense than grain based pastas, even whole wheat. Red lentil pasta contains nearly double the protein for less net carbs and calories. Red lentil pasta also contains higher levels of folate, copper, and iron.

Some recipes with gluten free pasta include Mediterranean Pasta Salad, Chicken Noodle Stew, Pasta with Healthier Clam Sauce, Pesto Goat Cheese Mac & Cheese, and Sundried Tomato Pasta Salad. Though you can easily substitute one type of pasta for another in any dish, whether it be shape (penne, rotini, spaghetti, etc.) or base ingredient (whole wheat, chickpea, red lentil, etc.)

Serving Size: 3/4 cup (56 g)

Last but not least, we have wild rice, which is technically a grass, not a true rice. It’s gluten free and higher in fiber compared to brown rice, though lower compared to most other whole grains. Wild rice is decently nutrient-dense, being a complete protein and a good source of vitamin B2, vitamin B3, vitamin B5, folate, magnesium, and manganese. Notably, wild rice is the best source of zinc, which helps to support immune health, as well as the creation of DNA and RNA. It has a nutty flavor and chewy texture, with more antioxidants than white rice.
Serving Size: 1/4 cup (40 g)

Nutritional Comparison
Scroll to the right to read information about every variation

References
This post may contain affiliate links
Ah grains, the base of the dreaded food pyramid. They get a lot of love, they get a lot of hate, but not much in the middle. Are grains good for you? Which ones? What nutrients do they provide? What if you're gluten free? I seek to answer all these questions today, and provide a grain of truth on the matter. As always, I am neither a doctor nor a nutritionist, just someone who's interested in nutrition science. Take everything I say with a grain of rice. I mean salt.


Other Posts in this Series
- Let's Meet The Meats
- I'm Nuts For Nuts
- I See Seeds In Your Future
- Beans Beans The Musical Fruit
- Going Bananas For Bananas
- Lettuce Turnip The Beet
- I'm Hooked On Fish
- A Grain Of Truth
- I'm Dying For Dairy


Contents
- Amaranth
- Barley
- Brown Rice
- Buckwheat
- Corn
- Couscous
- Farro
- Millet
- Oats
- Popcorn
- Quinoa
- Rye
- Spelt
- Vital Wheat Gluten
- White Flour
- White Pasta
- White Rice
- Whole Wheat Flour
- Whole Wheat Pasta
- Wild Rice
- Nutritional Comparison


Amaranth is technically a pseudograin (like quinoa and buckwheat), but it is eaten much like a grain. It’s tiny, nutty, and gluten-free. A 1/4 cup (48 g) serving of raw amaranth provides 178 calories, 7 g of complete protein, 3 g of fiber, and 28 g of net carbs. Amaranth is one of the most nutritious grains, being rich in vitamin B1, vitamin B2, vitamin B5, folate, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, selenium, and zinc. Amaranth may help in regulating muscle and nerve function, combatting chronic inflammation, and supporting immune system health.
------------------------------------------
Calories: 178
------------------------------------------
Total Fat: 3.4g (4 %)
Total Carbohydrate: 31.3g (12 %)
Fiber: 3.2g (12 %)
Net Carbs: 28.1g
Protein: 6.5g (13 %)
------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------
Vitamin B1 (Thiamin): 0.06mg (5 %)
Vitamin B9 (Folate): 39.4mcg (10 %)
------------------------------------------
Magnesium: 119mg (28 %)
Manganese: 1.6mg (70 %)
Phosphorus: 267mg (22 %)

Barley is one of the oldest cultivated grains, and a staple in soups, stews, and breads. Barley is a gluten containing grain, along with wheat and rye. It’s especially high in fiber, particularly beta-glucan, which can aid in lowering cholesterol and improving blood sugar control. 1/4 cup (50 g) of raw barley contains 176 calories, 5 g of protein, 8 g of fiber, and 39 g of net carbs. It’s also a good source of vitamin B1, vitamin B3, vitamin B6, copper, manganese, selenium, and zinc The glycemic index of barley is lower than most other grains due to it's high fiber content. It also is a good source of resistant starch, benefiting gut health.
------------------------------------------
Calories: 176
------------------------------------------
Total Fat: 0.6g (1 %)
Total Carbohydrate: 38.9g (14 %)
Fiber: 7.8g (28 %)
Net Carbs: 31.1g
Protein: 5.0g (10 %)
------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------
Vitamin B1 (Thiamin): 0.1mg (8 %)
Vitamin B9 (Folate): 11.5mcg (3 %)
------------------------------------------
Magnesium: 40mg (10 %)
Manganese: 0.66mg (29 %)
Phosphorus: 111mg (9 %)

Brown rice is simply white rice with the bran and germ left intact, which makes it higher in fiber and nutrients. 1/4 cup (46 g) of raw brown rice has 169 calories, 4 g of protein, 2 g of fiber, and 35 g of net carbs. Brown rice is a gluten free grain that is quite nutritious, though less so compared to some other whole grains (like amaranth and barley). Brown rice provides vitamin B1, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, selenium, and zinc. It also has antioxidants and heart health benefits that are stripped away in white rice, while having a chewier texture and nuttier flavor.
There's no shortage of ways to include brown rice (or any other whole grains) in your diet. Typically, when I write recipes, I write them without a carb (so just a protein and vegetable), so that way you can add whatever starch you like on the side. Below are some recipes with brown rice, either as a side dish or mixed into the main:
- Turkey & Rice Stuffed Bell Peppers
- Anti-Inflammatory Yellow(ish) Rice
- Cheesy Rice & Broccoli
- Nontraditional Kung Pao Chicken
- Dolmas (Stuffed Grape Leaves)
- Classic Rice and Beans
- Baked Rice and Beans with Vegetables

------------------------------------------
Calories: 169
------------------------------------------
Total Fat: 1.5g (2 %)
Total Carbohydrate: 35.1g (13 %)
Fiber: 1.7g (6 %)
Net Carbs: 33.4g
Protein: 3.5g (7 %)
------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------
Vitamin B1 (Thiamin): 0.25mg (21 %)
Vitamin B9 (Folate): 10.6mcg (3 %)
------------------------------------------
Magnesium: 53mg (13 %)
Manganese: 1.31mg (57 %)
Phosphorus: 143mg (12 %)

Buckwheat is another gluten free pseudograin, as are quinoa and amaranth. Despite the name, it’s not related to wheat at all; buckwheat is totally gluten free and also considered a complete protein. It's a moderate source of fiber, containing 4 g in a 1/4 cup (43 g) serving of raw buckwheat. Buckwheat is a strong source of vitamin B2, vitamin B3, vitamin B6, copper, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and zinc. It also contains unique compounds called rutin and quercetin, which act as powerful antioxidants that supports blood vessel health and reduce inflammation. Buckwheat also contains D-Chiro-Inositol, whch has a positive effect on managing blood sugar.
------------------------------------------
Calories: 147
------------------------------------------
Total Fat: 1.5g (2 %)
Total Carbohydrate: 30.7g (11 %)
Fiber: 4.3g (15 %)
Net Carbs: 26.4g
Protein: 5.7g (11 %)
------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------
Vitamin B1 (Thiamin): 0.04mg (3 %)
Vitamin B9 (Folate): 12.9mcg (3 %)
------------------------------------------
Magnesium: 99mg (24 %)
Manganese: 0.56mg (25 %)
Phosphorus: 149mg (12 %)

Corn is a staple gluten free grain that provides carbohydrates, some fiber, and antioxidants like lutein and zeaxanthin, which support eye health. Corn is quite lacking nutritionally, though it is one of the highest sources per gram of vitamin B6. That being said, whole corn and popcorn are much higher in nutrients than refined corn products, such as corn syrup, cornstarch, and corn oil. Just remember that corn is a grain/carb side, not a vegetable. I prefer to have my corn in the form of Roasted Corn on the Cob or Three Sisters - Squash, Beans, and Corn.

------------------------------------------
Calories: 73
------------------------------------------
Total Fat: 1.1g (2 %)
Total Carbohydrate: 15.9g (6 %)
Fiber: 1.7g (6 %)
Net Carbs: 14.2g
Protein: 2.8g (6 %)
------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------
Vitamin B1 (Thiamin): 0.13mg (11 %)
Vitamin B9 (Folate): 35.7mcg (9 %)
------------------------------------------
Magnesium: 31mg (8 %)
Manganese: 0.14mg (6 %)
Phosphorus: 76mg (6 %)

Couscous similar to many other grains, being a moderate source of the following nutrients: fiber, thiamin, niacin, vitamin B5, copper, magnesium, manganese, and phosphorus. These nutrients support energy metabolism, healthy digestion, and overall cell function, making couscous a light yet nourishing base for many meals.
Couscous is technically a pasta, being made of semolina wheat. That means that this delicious rice-like grain contains gluten. But it's more like rice than pasta; you cook couscous like you would rice, cooking until all the water has been absorbed. This is as opposed to pasta, which is boiled in excess water, and then subsequently drained off.

There's 2 different types of couscous: Moroccan and Israeli. Moroccan couscous is finer and fluffier, whereas Israeli (Pearl) couscous is bigger and more pasta-like. My preferred way to eat couscous is to cook Moroccan couscous with beans and diced tomatoes, like I do in my Tomato and Bean Couscous.

------------------------------------------
Calories: 211
------------------------------------------
Total Fat: 0.4g (1 %)
Total Carbohydrate: 43.4g (16 %)
Fiber: 2.8g (10 %)
Net Carbs: 40.6g
Protein: 7.1g (15 %)
------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------
Vitamin B1 (Thiamin): 0.09mg (8 %)
Vitamin B9 (Folate): 11.2mcg (3 %)
------------------------------------------
Magnesium: 25mg (6 %)
Manganese: 0.44mg (19 %)
Phosphorus: 95mg (8 %)

Farro is an ancient wheat based grain that cooks and tastes like brown rice. This gluten containing whole grain is a great addition to your diet, being high in fiber and protein for a side dish, as well as thiamin , niacin, vitamin B6, copper, magnesium, phosphorus, and zinc. Consider checking out my Chicken Farro Bowls with Goat Cheese for a delicious and complete meal featuring farro, with over 50 g of protein in under 550 calories.

------------------------------------------
Calories: 155
------------------------------------------
Total Fat: 1.4g (2 %)
Total Carbohydrate: 32.4g (12 %)
Fiber: 4.3g (15 %)
Net Carbs: 28.1g
Protein: 5.7g (11 %)
------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------
Vitamin B1 (Thiamin): 0.17mg (14 %)
Vitamin B9 (Folate): 18.9mcg (5 %)
------------------------------------------
Magnesium: 54mg (13 %)
Manganese: 1.75mg (76 %)
Phosphorus: 166mg (14 %)

Millet is a gluten free grain high in vitamin B1, vitamin B2, vitamin B3, vitamin B6, folate, copper, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and zinc. It's a decent source of plant protein, with 6 g in a 189 calorie serving, as well as 4 g of fiber. It's lower glycemic index value may be helpful in combatting insulin resistance, and its carotenoids may benefit wound healing. As it's gluten free, millet flour is great in gluten free baking; see my Gluten Free Millet Bread for more.
------------------------------------------
Calories: 189
------------------------------------------
Total Fat: 2.1g (3 %)
Total Carbohydrate: 36.4g (13 %)
Fiber: 4.3g (15 %)
Net Carbs: 32.1g
Protein: 5.5g (11 %)
------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------
Vitamin B1 (Thiamin): 0.21mg (18 %)
Vitamin B9 (Folate): 42.5mcg (11 %)
------------------------------------------
Magnesium: 57mg (14 %)
Manganese: 0.82mg (36 %)
Phosphorus: 143mg (12 %)

Ah, my beloved oats. Not only are they gluten free, but oats are rich in a fiber known as beta-glucan, which can help lower cholesterol and steady blood sugar levels. A 1/4 cup (40 g) of raw oats contains 4 g of fiber in just 152 calories, along with 5 g of protein. Oats are the best source of vitamin B1 and also contain notable amounts of vitamin B5, copper, iron, manganese, phosphorus, selenium, and zinc. Additionally, oats contain avenathramides, which are antioxidants linked to reduced inflammation and lower blood pressure.
I don't think there's an ingredient I use more in baking than oats, as long as you're not counting vanilla or salt or something. Between rolled oats, quick oats, and oat flour, oats are a staple part in my desserts, protein snacks, and breakfasts. Check out my myriad of recipes with oats below:
- Bread
- Breakfast
- Oatmeal Berry Breakfast Bars
- Hi Mom, Here's Your Oatmeal
- Stovetop Apple Oatmeal
- Pumpkin Spice Apple Bread
- Banana Protein Pancakes
- Overnight Oats with no Protein Powder
- Strawberry Chia Protein Oatmeal
- Yogurt Free Protein Oats
- Bigger Boi Oatmeal
- Banana Nut Bread Protein Overnight Oats
- Oatmeal Banana Mini Muffins
- Pumpkin Protein Pancakes
- Very Vic
- Peanut Butter Punch Protein Overnight Oats
- Berry Delicious Protein Overnight Oats
- Peanut Butter & Jelly Muffins
- Pumpkin Pie Protein Overnight Oats
- Reese's Protein Overnight Oats
- Snacks
- No Bake Energy Bites
- Peanut Butter Cocoa Bites
- Air Fryer Biscotti
- Peanut Butter Banana Granola Bars
- Low Sugar Granola
- Gluten Free Graham Crackers
- Chocolate Covered Truffles
- Chocolate Yogurt Kerfuffles
- Two Ingredient Oat Cookies
- Protein Powder
- No Nut Protein Banana Bread
- Copycat Barebell Protein Bars
- Microwave Protein Mug Cake
- PB&J Protein PopTart
- Protein Pumpkin Loaf
- Protein Banana Nut Bread
- Protein Apple Bread
- Chickpea Chows
- Layered Protein Carrot Cake
- Nice Cream Sandwiches
- Dessert
- Naturally Sweetened Oatmeal Raisin Cookies
- Dye Free Rainbow Cookies
- Homemade Thin Mint Cookies
- No Bake Homemade Tiramisu
- Date Cuccidati Cookies
- 7-Layer Bars
- Edible Cookie Dough Bites
- Healthier Graham Cracker Pie Crust
- Frosted Pumpkin Cake
- No Bake Cheesecake Bars
- Peanut Butter Fudge Bars
- Sweet Potato Blondies
- Sugar Free Apple Pie
- Dual Bean Date Brookies
- Chickpea Date Blondies
- Black Bean Date Brownies
- Apple Crumble with Oats
- Healthier Cut Out Cookies
- Honey Sweetened Peanut Butter Cookies
- Oatmeal Chocolate Chip Cookies
- Sweet Potato Brownies (GF)
- Coconut Macarooons with Honey
- Peanut Butter Banana Bars
- No Bake Cookie Bars
- Double Chocolate Banana Bread
- Chocolate Chip Cookie Skillet
- Other




------------------------------------------
Calories: 152
------------------------------------------
Total Fat: 2.6g (3 %)
Total Carbohydrate: 27.1g (10 %)
Fiber: 4.0g (14 %)
Net Carbs: 23.1g
Protein: 5.3g (10 %)
------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------
Vitamin B1 (Thiamin): 0.18mg (15 %)
Vitamin B9 (Folate): 12.8mcg (3 %)
------------------------------------------
Magnesium: 55mg (13 %)
Manganese: 1.45mg (63 %)
Phosphorus: 164mg (13 %)

When air-popped, popcorn is a great gluten free, whole grain snack that’s low in calories and high in fiber. Popcorn is one of the best volume foods, just 3 tbsp (40 g) of raw popcorn becomes over 7 cups of cooked popcorn. It also contains antioxidants like polyphenols, but it’s best without excess butter or salt. Check out my Healthy Microwave Popcorn for a significantly healthier alternative to movie theater or microwave popcorn, being free of tons of fat and added chemicals.
------------------------------------------
Calories: 154
------------------------------------------
Total Fat: 1.8g (2 %)
Total Carbohydrate: 31.0g (11 %)
Fiber: 5.8g (20 %)
Net Carbs: 25.2g
Protein: 5.2g (10 %)
------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------
Vitamin B1 (Thiamin): 0.04mg (4 %)
Vitamin B9 (Folate): 12.4mcg (3 %)
------------------------------------------
Magnesium: 57mg (14 %)
Manganese: 0.0mg (0 %)
Phosphorus: 143mg (12 %)

Quinoa is a gluten-free pseudograin (like amaranth and buckwheat) notable for being a complete protein, as it contains all 9 essential amino acids. It’s surprisingly higher in protein (6 g) than fiber (3 g) with 158 calories in a 1/4 cup (43 g) serving. Quinoa is a good source of many B vitamins, such as B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, and B9. Quinoa is also rich in vitamin E, choline, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, selenium, and zinc. Quinoa is also a good source of the antioxidants kaempferol and quercetic, which help protect against chronic disease and lower inflammation.
Quinoa is one of the healthiest side dishes out there, and cooks just like rice in half the time. In any recipe calling for white or brown rice, you can simple swap them for quinoa for extra nutrition and a nuttier flavor. Check out my No Butter Chicken with Quinoa and Date Night Superfood Bowls for some quinoa based recipes.
------------------------------------------
Calories: 158
------------------------------------------
Total Fat: 2.6g (3 %)
Total Carbohydrate: 27.6g (10 %)
Fiber: 3.0g (11 %)
Net Carbs: 24.6g
Protein: 6.1g (12 %)
------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------
Vitamin B1 (Thiamin): 0.15mg (13 %)
Vitamin B9 (Folate): 79.1mcg (20 %)
------------------------------------------
Magnesium: 85mg (20 %)
Manganese: 0.87mg (38 %)
Phosphorus: 197mg (16 %)

Rye, along with wheat and barley, is a gluten containing whole grain that provides a dense source of fiber (6 g) and protein (4 g) in 142 calories. The high fiber content in rye supports healthy digestion and aids in satiety, and rye can also help lower LDL levels. It is a good source of the vitamins B1, B2, B3, B6, and B9. Moreover, rye is a good source of copper, manganese, selenium, and zinc. It has a stronger flavor and may support better blood sugar control than refined wheat.
------------------------------------------
Calories: 142
------------------------------------------
Total Fat: 0.7g (1 %)
Total Carbohydrate: 31.9g (12 %)
Fiber: 6.3g (23 %)
Net Carbs: 25.6g
Protein: 4.3g (9 %)
------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------
Vitamin B1 (Thiamin): 0.13mg (11 %)
Vitamin B9 (Folate): 16.0mcg (4 %)
------------------------------------------
Magnesium: 46mg (11 %)
Manganese: 1.08mg (47 %)
Phosphorus: 139mg (11 %)

Spelt is an ancient variety of wheat (meaning it's not gluten free) that contains fiber, protein, and minerals like copper, iron, manganese, selenium, and zinc. Like most other grains, spelt is a good source of B vitamins, notably B1, B3, B6, and B9. It still has gluten, but some find it easier to digest than modern wheat.
------------------------------------------
Calories: 149
------------------------------------------
Total Fat: 1.1g (1 %)
Total Carbohydrate: 30.9g (11 %)
Fiber: 4.7g (17 %)
Net Carbs: 26.2g
Protein: 6.4g (13 %)
------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------
Vitamin B1 (Thiamin): 0.16mg (13 %)
Vitamin B9 (Folate): 19.8mcg (5 %)
------------------------------------------
Magnesium: 60mg (14 %)
Manganese: 1.31mg (57 %)
Phosphorus: 176mg (14 %)

Vital wheat gluten is the concentrated protein extracted from wheat. It's basically the anti gluten free flour; it's made up of entirely gluten. Vital wheat gluten is what gives seitan its chewy texture, and is very high in protein while being low in net carbs. Gram for gram, vital wheat gluten basically has the macros of protein powder, though the protein quality of gluten is extremely poor.
In bread making though, vital wheat gluten is a great ingredient that leads to a lighter, fluffier loaf. When swapping out white flour in place of whole wheat, I like to add a little vital wheat gluten to the dough, which results in a less dense loaf of bread. Below are a few recipes utilizing vital wheat gluten:
- Onion Soup Bread
- Easy Pizza Dough
- No Yeast Burger Buns
- Whole Wheat Baguettes
- Whole Wheat Sweet Potato Loaf
- Whole Wheat Pita Bread
- Whole Wheat Hot Pretzels
- Home Oven Baked Pizza
- 100% Whole Wheat Bread

------------------------------------------
Calories: 111
------------------------------------------
Total Fat: 0.6g (1 %)
Total Carbohydrate: 4.1g (2 %)
Fiber: 0.2g (1 %)
Net Carbs: 3.9g
Protein: 22.6g (45 %)
------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------
Vitamin B1 (Thiamin): 0.15mg (13 %)
Vitamin B9 (Folate): 13.2mcg (3 %)
------------------------------------------
Magnesium: 8mg (2 %)
Manganese: 0.0mg (0 %)
Phosphorus: 78mg (6 %)

White flour is to whole wheat flour what white rice is to brown rice. Besides white flour, it's also known under the names all purpose flour, bread flour, cake flour, etc. As with white rice, white flour needs to be enriched with vitamins and minerals, because they've all been stripped away. White flour has little to no fiber and has a glycemic index of 85, higher than white sugar! And as you are likely aware, white flour contains gluten.
------------------------------------------
Calories: 113
------------------------------------------
Total Fat: 0.3g (0 %)
Total Carbohydrate: 23.7g (9 %)
Fiber: 0.8g (3 %)
Net Carbs: 22.9g
Protein: 3.2g (7 %)
------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------
Vitamin B1 (Thiamin): 0.04mg (3 %)
Vitamin B9 (Folate): 8.1mcg (2 %)
------------------------------------------
Magnesium: 7mg (2 %)
Manganese: 0.21mg (9 %)
Phosphorus: 33mg (3 %)

White pasta is a refined wheat-based grain product that contains gluten. A typical serving of pasta consists about about 3/4 cup (2 oz, 56 g) of raw pasta, or about 2 cups (135 g) of cooked pasta. Each serving contains about 200 calories with 2 g fiber and 7 g of protein. Being a refined white flour grain product, standard white pasta is nutritionally quite lacking, containing more empty calories than actual nutrition. Compared to whole wheat pasta, white pasta is significantly lower in B vitamins, iron, magnesium, and potassium.
------------------------------------------
Calories: 208
------------------------------------------
Total Fat: 0.8g (1 %)
Total Carbohydrate: 41.8g (15 %)
Fiber: 1.8g (6 %)
Net Carbs: 40.0g
Protein: 7.3g (15 %)
------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------
Vitamin B1 (Thiamin): 0.05mg (4 %)
Vitamin B9 (Folate): 10.1mcg (2 %)
------------------------------------------
Magnesium: 30mg (7 %)
Manganese: 0.51mg (22 %)
Phosphorus: 106mg (8 %)

White rice is a gluten free refined grain with most of its fiber and micronutrients removed. White rice is often enriched with vitamins and minerals. Do you know why? Because it's so devoid of them in the first place. All the health benefits of the whole rice grain have been stripped away, leaving nothing but refined white starch with a low fiber content and a high glycemic index. When in doubt, swap out white for brown rice.
------------------------------------------
Calories: 176
------------------------------------------
Total Fat: 0.3g (0 %)
Total Carbohydrate: 38.9g (14 %)
Fiber: 0.0g (0 %)
Net Carbs: 38.9g
Protein: 3.2g (6 %)
------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------
Vitamin B1 (Thiamin): 0.03mg (3 %)
Vitamin B9 (Folate): 4.4mcg (1 %)
------------------------------------------
Magnesium: 17mg (4 %)
Manganese: 0.54mg (24 %)
Phosphorus: 53mg (4 %)

Whole wheat flour retains the bran and germ, unlike white flour, making it higher in fiber and lower in net carbs. Containing all the nutrients of the whole wheat kernel, whole wheat flour is a rich source of vitamin B1, vitamin B3, vitamin B6, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, selenium, and zinc. Whole wheat supports digestive health and provides steadier blood sugar control compared to refined wheat. It also contains phenolic compounds known as lignans and tocopherols, which can help combat chronic inflammation. Whole wheat flour does contain gluten, so be on the lookout for that if you have Celiac.
I will always swap out white flour whole wheat for better nutrition and taste. In bread making, I like to add a little vital wheat gluten to the dough, which results in a less dense loaf of bread. Below are a few recipes utilizing whole wheat flour:
- Copycat Triscuit Crackers
- Hot Honey Cornbread
- Onion Soup Bread
- Whole Wheat Deep Dish Pizza Pie
- Easy Pizza Dough
- Whole Wheat Beer Bread
- No Yeast Burger Buns
- Whole Wheat Baguettes
- Fluffy Protein Cinnamon Rolls
- Whole Wheat and Oat Flour Irish Soda Bread
- Whole Wheat Sweet Potato Loaf
- Whole Wheat Pita Bread
- Whole Wheat Hot Pretzels
- Whole Wheat Breakfast Crepes
- Home Oven Baked Pizza
- Peanut Butter Bread
- Oat-Wheat Tortillas
- 100% Whole Wheat Bread

------------------------------------------
Calories: 105
------------------------------------------
Total Fat: 0.8g (1 %)
Total Carbohydrate: 22.3g (8 %)
Fiber: 3.3g (12 %)
Net Carbs: 19.0g
Protein: 4.1g (8 %)
------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------
Vitamin B1 (Thiamin): 0.16mg (13 %)
Vitamin B9 (Folate): 13.6mcg (3 %)
------------------------------------------
Magnesium: 42mg (10 %)
Manganese: 1.26mg (55 %)
Phosphorus: 111mg (9 %)

Whole wheat pasta is a less refined wheat-based grain product that contains gluten. When considering pasta options, whole wheat pasta is a signifcantly better source than standard white pasta. Whole wheat pasta contains triple the amount of fiber, leading to less net carbs and calories.
Additionally, whole wheat pasta is a moderate source of B vitamins, such as B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, and B9. Whole wheat pasta is a good source of many minerals, namely copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, selenium, and zinc.
The typical way to eat pasta would be as a side dish with a sauce on top of it. Classic options include my Simple Pasta Sauce, Creamy Pesto Dip, Lightened EVOO Pesto, Avocado Pesto, Oil Free Bail Pesto, Pesto Classico, and Gooey Cheese Sauce.

As for other pasta based dishes, whole wheat pasta can be a great basis for many meals, namely a Penne and Meat Casserole Bake, Two Ingredient Mac & Cheese, or Viral Baked Feta Pasta.

When I'm choosing a pasta though, I'll typically opt for either red lentil or chickpea pasta. Not only are these both gluten free, but legume based pastas are more nutrient dense than grain based pastas, even whole wheat. Red lentil pasta contains nearly double the protein for less net carbs and calories. Red lentil pasta also contains higher levels of folate, copper, and iron.

Some recipes with gluten free pasta include Mediterranean Pasta Salad, Chicken Noodle Stew, Pasta with Healthier Clam Sauce, Pesto Goat Cheese Mac & Cheese, and Sundried Tomato Pasta Salad. Though you can easily substitute one type of pasta for another in any dish, whether it be shape (penne, rotini, spaghetti, etc.) or base ingredient (whole wheat, chickpea, red lentil, etc.)

------------------------------------------
Calories: 197
------------------------------------------
Total Fat: 1.6g (2 %)
Total Carbohydrate: 41.1g (15 %)
Fiber: 5.2g (18 %)
Net Carbs: 35.9g
Protein: 7.8g (16 %)
------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------
Vitamin B1 (Thiamin): 0.23mg (19 %)
Vitamin B9 (Folate): 38.6mcg (10 %)
------------------------------------------
Magnesium: 72mg (17 %)
Manganese: 1.67mg (73 %)
Phosphorus: 192mg (15 %)

Last but not least, we have wild rice, which is technically a grass, not a true rice. It’s gluten free and higher in fiber compared to brown rice, though lower compared to most other whole grains. Wild rice is decently nutrient-dense, being a complete protein and a good source of vitamin B2, vitamin B3, vitamin B5, folate, magnesium, and manganese. Notably, wild rice is the best source of zinc, which helps to support immune health, as well as the creation of DNA and RNA. It has a nutty flavor and chewy texture, with more antioxidants than white rice.
------------------------------------------
Calories: 143
------------------------------------------
Total Fat: 0.4g (0 %)
Total Carbohydrate: 30.0g (11 %)
Fiber: 2.5g (9 %)
Net Carbs: 27.5g
Protein: 5.9g (12 %)
------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------
Vitamin B1 (Thiamin): 0.05mg (4 %)
Vitamin B9 (Folate): 38.0mcg (10 %)
------------------------------------------
Magnesium: 71mg (17 %)
Manganese: 0.53mg (23 %)
Phosphorus: 173mg (14 %)

Nutritional Comparison
| Nutrient | Amaranth | Barley | Brown Rice | Buckwheat | Corn | Couscous | Farro | Millet | Oats | Popcorn | Quinoa | Rye | Spelt | Vital Wheat Gluten | White Flour | White Pasta | White Rice | Whole Wheat Flour | Whole Wheat Pasta | Wild Rice |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serving Size | 48 g | 50 g | 46 g | 43 g | 85 g | 56 g | 45 g | 50 g | 40 g | 40 g | 43 g | 42 g | 44 g | 30 g | 31 g | 56 g | 49 g | 31 g | 56 g | 40 g |
| Calories | 178 | 176 | 169 | 147 | 73 | 211 | 155 | 189 | 152 | 154 | 158 | 142 | 149 | 111 | 113 | 208 | 176 | 105 | 197 | 143 |
| Fat | 3.4 g | 0.6 g | 1.5 g | 1.5 g | 1.2 g | 0.3 g | 1.4 g | 2.1 g | 2.6 g | 1.8 g | 2.6 g | 0.7 g | 1.1 g | 0.6 g | 0.3 g | 0.8 g | 0.3 g | 0.8 g | 1.6 g | 0.4 g |
| Carbs | 31.3 g | 38.9 g | 35.1 g | 30.7 g | 15.9 g | 43.3 g | 32.4 g | 36.5 g | 27.1 g | 31.0 g | 27.6 g | 31.9 g | 30.9 g | 4.1 g | 23.7 g | 41.8 g | 38.9 g | 22.3 g | 41.1 g | 30.0 g |
| Net Carbs | 28.1 g | 31.1 g | 33.4 g | 26.4 g | 14.2 g | 40.5 g | 28.1 g | 32.2 g | 23.0 g | 25.2 g | 24.6 g | 25.5 g | 26.2 g | 4.0 g | 22.8 g | 40.0 g | 38.9 g | 19.0 g | 36.0 g | 27.5 g |
| Fiber | 3.2 g | 7.8 g | 1.7 g | 4.3 g | 1.7 g | 2.8 g | 4.3 g | 4.3 g | 4.0 g | 5.8 g | 3.0 g | 6.3 g | 4.7 g | 0.2 g | 0.8 g | 1.8 g | 0.0 g | 3.3 g | 5.2 g | 2.5 g |
| Protein | 6.5 g | 5.0 g | 3.5 g | 5.7 g | 2.8 g | 7.2 g | 5.7 g | 5.5 g | 5.3 g | 5.2 g | 6.1 g | 4.3 g | 6.4 g | 22.6 g | 3.2 g | 7.3 g | 3.2 g | 4.1 g | 7.8 g | 5.9 g |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.06 mg | 0.1 mg | 0.25 mg | 0.04 mg | 0.14 mg | 0.09 mg | 0.17 mg | 0.21 mg | 0.18 mg | 0.04 mg | 0.15 mg | 0.13 mg | 0.16 mg | 0.15 mg | 0.04 mg | 0.05 mg | 0.03 mg | 0.16 mg | 0.23 mg | 0.05 mg |
| Vitamin B9 | 39.4 mcg | 11.5 mcg | 10.6 mcg | 12.9 mcg | 35.7 mcg | 11.2 mcg | 18.9 mcg | 42.5 mcg | 12.8 mcg | 12.4 mcg | 79.1 mcg | 16.0 mcg | 19.8 mcg | 13.2 mcg | 8.1 mcg | 10.1 mcg | 4.4 mcg | 13.6 mcg | 38.6 mcg | 38.0 mcg |
| Magnesium | 119 mg | 40 mg | 53 mg | 99 mg | 31 mg | 25 mg | 54 mg | 57 mg | 55 mg | 57 mg | 85 mg | 46 mg | 60 mg | 8 mg | 7 mg | 30 mg | 17 mg | 42 mg | 72 mg | 71 mg |
| Manganese | 1.6 mg | 0.66 mg | 1.31 mg | 0.56 mg | 0.14 mg | 0.44 mg | 1.75 mg | 0.82 mg | 1.45 mg | 0.0 mg | 0.87 mg | 1.08 mg | 1.31 mg | 0.0 mg | 0.21 mg | 0.52 mg | 0.54 mg | 1.26 mg | 1.67 mg | 0.53 mg |
| Phosphorus | 267 mg | 111 mg | 143 mg | 149 mg | 76 mg | 95 mg | 166 mg | 143 mg | 164 mg | 143 mg | 197 mg | 139 mg | 176 mg | 78 mg | 33 mg | 106 mg | 53 mg | 111 mg | 192 mg | 173 mg |

References

